13/09/2021
What is a floor area ratio?
A floor area ratio (or FAR) is a type of planning control that sets a specific amount of development that can occur on a site. The floor area ratio is the ratio of a new building’s total floor area in relation to the size of the site it is being built on.
When combined with other built form controls, it allows for variation in the height and shape of buildings. This will help to ensure that new development is responsive to its site and the characteristics of an area. The diagrams below explain the concept of floor area ratios and how they can result in different building types. For example, a floor area ratio of 4:1 allows for a total floor area up to four times the size of the site itself. This could be up to four storeys if 100 per cent of the site is developed or eight storeys if only half the site is developed. For larger sites, a floor area ratio combined with other built form controls allows for variation in the height and shape of buildings while also enabling the delivery of new streets and open spaces. Some of the benefits of floor area ratios are they:
- can often be aligned to the overall population or employment target for an area
- can help deliver a range of building typologies, helping to deliver a range of uses and provide visual interest
- set realistic and clear expectations about the potential development yield on a site
- enable flexibility for an architect to choose how they organise their building layout and form on their site within a preferred built form envelope, and focus on design quality rather than yield
- have a direct relationship with the size of a site and can therefore be relatively easy to communicate
- can help deliver a mix of uses with guidance for minimum floor areas for a range of different uses
- provide a clear and consistent measure to support efficient decision making.
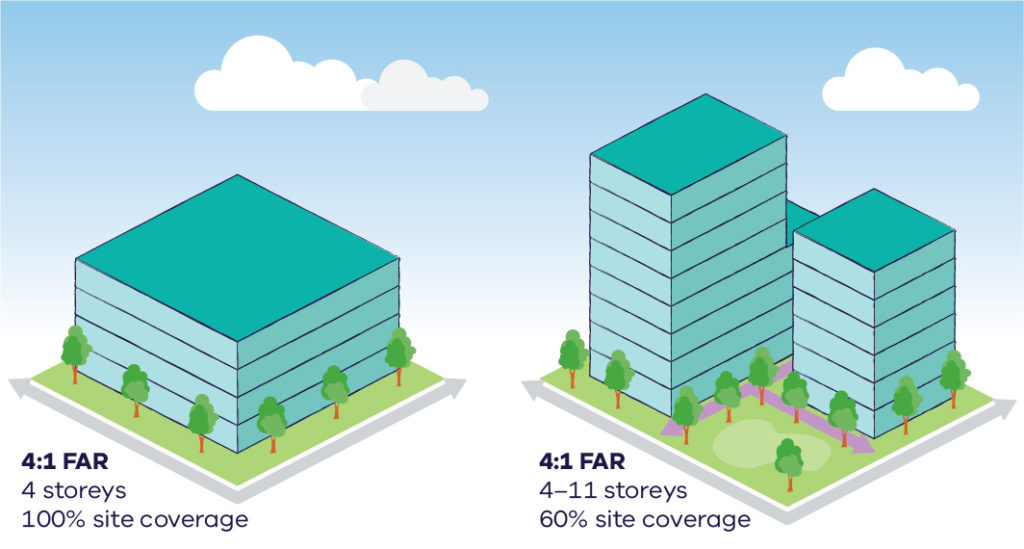
An example diagram of floor area ratios (FARs) showing two different storey buildings.
